- Discover what MOIC (Multiple On Invested Capital) means and why it’s a vital metric in business acquisitions.
- Learn how to calculate MOIC with a straightforward formula.
- Understand the difference between Net and Gross MOIC and what each represents.
- Gain insights into the factors that can influence MOIC, such as market conditions and timing.
- Compare MOIC with other key financial metrics like ROI, IRR, and TVPI.
Multiple On Invested Capital (MOIC) is a crucial metric for investors, venture capitalists, and entrepreneurs involved in the valuation and acquisition of businesses.
This article aims to shed light on various aspects of MOIC, including its definition, formula, and its importance in evaluating the financial health of an investment.
We also explore the various factors that can influence MOIC, its comparison with other key metrics like ROI and IRR, and some of its limitations.
What is MOIC?
MOIC is used to assess the return on investment (ROI) in a business venture, particularly in the context of acquisitions and private equity investments. You might also see it referred to by the synonyms MoM (Multiple on Money) or Coc (Cash-on-Cash Return).
MOIC essentially quantifies how much an investor has made back relative to the original investment.
For example, a MOIC of 3x would indicate that the investor has tripled their initial investment.
In the context of business acquisition, MOIC serves as a lens through which both the buyer and the seller can evaluate the financial attractiveness of the deal.
It provides a snapshot of the returns the acquisition might generate, thereby guiding investment decisions.
MOIC Formula & Calculation
The formula to calculate MOIC is fairly straightforward:
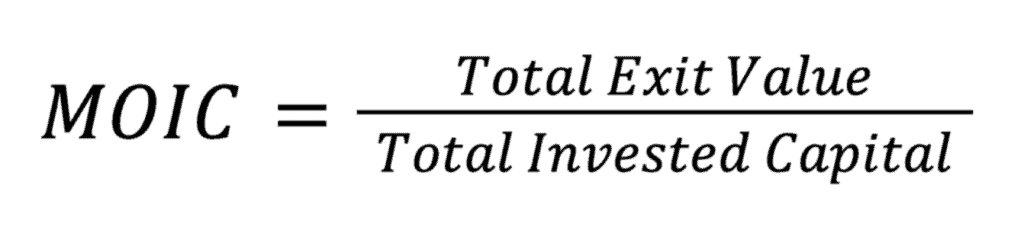
- Total Exit Value: This is the amount that an investment is worth at the time of its exit. It includes not just the selling price of the acquired entity but may also include any dividends or additional financial benefits accrued during the period of ownership.
- Total Invested Capital: This is the aggregate amount of capital that was invested in the business. It includes the purchase price and any additional capital expenditures or operational costs invested to grow or sustain the business.
By dividing the Total Exit Value by the Total Invested Capital, MOIC gives you a multiplier that represents the profitability of your investment.
Net vs Gross MOIC
The terms Net and Gross MOIC often surface when discussing this metric.
Net MOIC takes into account not just the Total Exit Value and Total Invested Capital, but also includes fees and expenses related to the investment.
This provides a more accurate picture of the actual return.
Gross MOIC, on the other hand, is calculated without considering these additional costs. As a result, it may present a more optimistic view of the investment’s profitability.
Importance of MOIC

MOIC is a critical metric for investors and entrepreneurs alike as it offers a straightforward way to assess the profitability and success of an investment.
Unlike other financial metrics, MOIC distills the complexity of an investment outcome into a single, easily understandable figure.
For investors, a higher MOIC can signal a successful investment strategy, validating their decisions and boosting their confidence in future investments.
It also aids in portfolio management, helping investors understand which assets are over- or under-performing.
MOIC is of paramount importance when it comes to small business acquisition as well.
Unlike larger corporations where acquisitions might be part of a broader portfolio strategy, small business acquisitions often represent a significant, sometimes even transformational, event for both the buyer and the seller.
Therefore, ensuring that the investment is financially sound is of utmost importance, and this is where MOIC comes into play.
For the buyer, particularly if they are an entrepreneur or a small business owner themselves, the acquisition could be a pivotal move that consumes a large portion of their available capital.
A strong MOIC would indicate that the investment is likely to be profitable, signaling less risk associated with the transaction.
Since small businesses often operate on tighter margins and have less room for error, knowing that an investment is likely to yield a high return can make the acquisition far less risky and more strategically sound.
For the seller, a small business is often the result of years, if not decades, of hard work and investment.
Demonstrating a high MOIC can not only justify a higher selling price, but also make the business more attractive to potential buyers.
This can be especially critical in cases where the seller is looking to retire or pivot into a different venture and needs the capital from the sale for their next phase of life or business activity.
Factors Influencing MOIC
A number of factors can affect MOIC, including:
- Market Conditions: Economic booms or downturns can drastically affect the exit value of an investment. Bull markets may inflate MOIC values, while bear markets can depress them.
- Industry: The sector in which the investment lies can also dictate MOIC. High-growth industries like technology might offer higher MOICs due to rapid valuation growth, while more stable industries might present lower, though consistent, MOIC values.
- Timing of Investments: Investing at the start of a growth phase can yield a higher MOIC compared to investing at maturity or decline.
MOIC vs. Other Metrics
While MOIC provides a clear picture of the return relative to the initial capital invested, other metrics offer different perspectives on investment returns:
- MOIC vs. ROI (Return on Investment): ROI measures the percentage return on a particular investment relative to its cost. While both metrics aim to gauge the profitability of an investment, MOIC gives a multiple of the capital invested, while ROI provides a percentage. For instance, an ROI of 200% corresponds to an MOIC of 3x.
- MOIC vs. IRR (Internal Rate of Return): IRR is the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows equal to zero. While MOIC indicates how many times the initial investment was multiplied, IRR indicates the annualized effective compounded return rate. IRR considers the time value of money, offering a more comprehensive view of the investment’s performance over time. IRR is a more accurate measure of return, but it is difficult to grasp intuitively.
- MOIC vs. TVPI (Total Value to Paid-In (TVPI) is another metric that combines the residual value of an investment and the distributions received relative to the amount paid in. Like MOIC, TVPI provides a multiple, but it’s a broader measure because it accounts for both realized and unrealized returns.
Limitations of MOIC

While MOIC offers valuable insights, it has its limitations:
- Time Value of Money: MOIC does not consider the duration of the investment. Getting a 2x return in one year vs. ten years is significantly different in terms of annualized returns, but MOIC treats them the same.
- Excludes Non-Cash Returns: MOIC is limited to tangible cash returns, ignoring other forms of returns like stock or in-kind dividends.
- Ignores Risk and Volatility: It does not factor in the risk associated with an investment. Two investments with the same MOIC might have vastly different risk profiles.
- Limited to Cash Flow Focus: MOIC does not consider the total value created, focusing solely on cash returns relative to the initial investment.
- Does Not Consider Reinvestment: The metric does not account for the potential returns that could have been generated if the initial investment was reinvested elsewhere.
Seek Professional Expertise with Acquira
If you’re looking for help to determine an accurate MOIC, consider Acquira’s proprietary Due Diligence Process.
From financial health to customer overview and legal considerations, Acquira’s checklist of 297 items ensures that you leave no stone unturned.
This comprehensive approach significantly alleviates the stress associated with the unknowns of business acquisition.
Acquira’s due diligence checklist incorporates a variety of questions that can influence MOIC.
Whether it’s the financial overview to assess the net profitability of the business, or the competition overview to gauge market saturation and potential growth, each of these 297 items can potentially affect MOIC, and by extension, the wisdom of proceeding with the acquisition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A good MOIC multiple varies depending on the industry and investment context. Generally, a higher MOIC indicates better investment returns. In venture capital and private equity, a MOIC of 2x to 3x or more is often considered strong.
No, MOIC does not typically include interest. It’s calculated by dividing the total exit value by the total invested capital, focusing purely on the principal amount invested and returned.
A 1x MOIC means you’ve essentially broken even on your investment. Your total exit value is equal to the total capital you initially invested, without any profit or loss.
Generally, MOIC does not include fees like transaction or management fees. It’s designed to measure the core profitability of an investment, without external costs affecting its value.
Conclusion
Understanding MOIC is essential for anyone involved in the financial evaluation of business ventures.
Whether you’re an investor seeking profitable opportunities, or an entrepreneur looking to understand the value of your business, MOIC serves as a straightforward yet powerful tool for gauging success.
However, it’s crucial to remember that MOIC offers only a snapshot of investment profitability and not the full picture.
Always consider other financial metrics and perform comprehensive due diligence to make the most informed decisions.
If you’re an aspiring entrepreneur who wants to level up their game with a deeper understanding of key financial terms like MOIC, consider enrolling in Acquira’s Accelerator program where you’ll get MBA-level training that could see you as the owner-operator of a $1MM/year cash-flowing business in as little as seven months.
You’ll get access to Acquira’s business experts as well as connect with a growing cadre of like-minded acquisition entrepreneurs.
Sign up with the form below but space is limited.
Key Takeaways
- MOIC quantifies your returns relative to your initial investment, making it a crucial metric in the acquisition landscape.
- The formula for MOIC is Total Exit Value divided by Total Invested Capital.
- Net MOIC provides a more accurate picture of returns by including fees and expenses.
- While MOIC offers a clear snapshot of an investment’s profitability, it has limitations like ignoring the time value of money and risk factors.
- For a well-rounded financial assessment, complement MOIC with other metrics and comprehensive due diligence.
Acquira specializes in seamless business succession and acquisition. We guide entrepreneurs in acquiring businesses and investing in their growth and success. Our focus is on creating a lasting, positive impact for owners, employees, and the community through each transition.



